Products
- Capacitor Networks, Arrays(2073)
- Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors(119232)
- Tantalum Capacitors(106098)
- Ceramic Capacitors(802073)
- Electric Double Layer Capacitors (EDLC), Supercapacitors(2508)
- Film Capacitors(165215)
- Mica and PTFE Capacitors(9477)
- Trimmers, Variable Capacitors(1755)
- Thin Film Capacitors(3401)
- Niobium Oxide Capacitors(219)
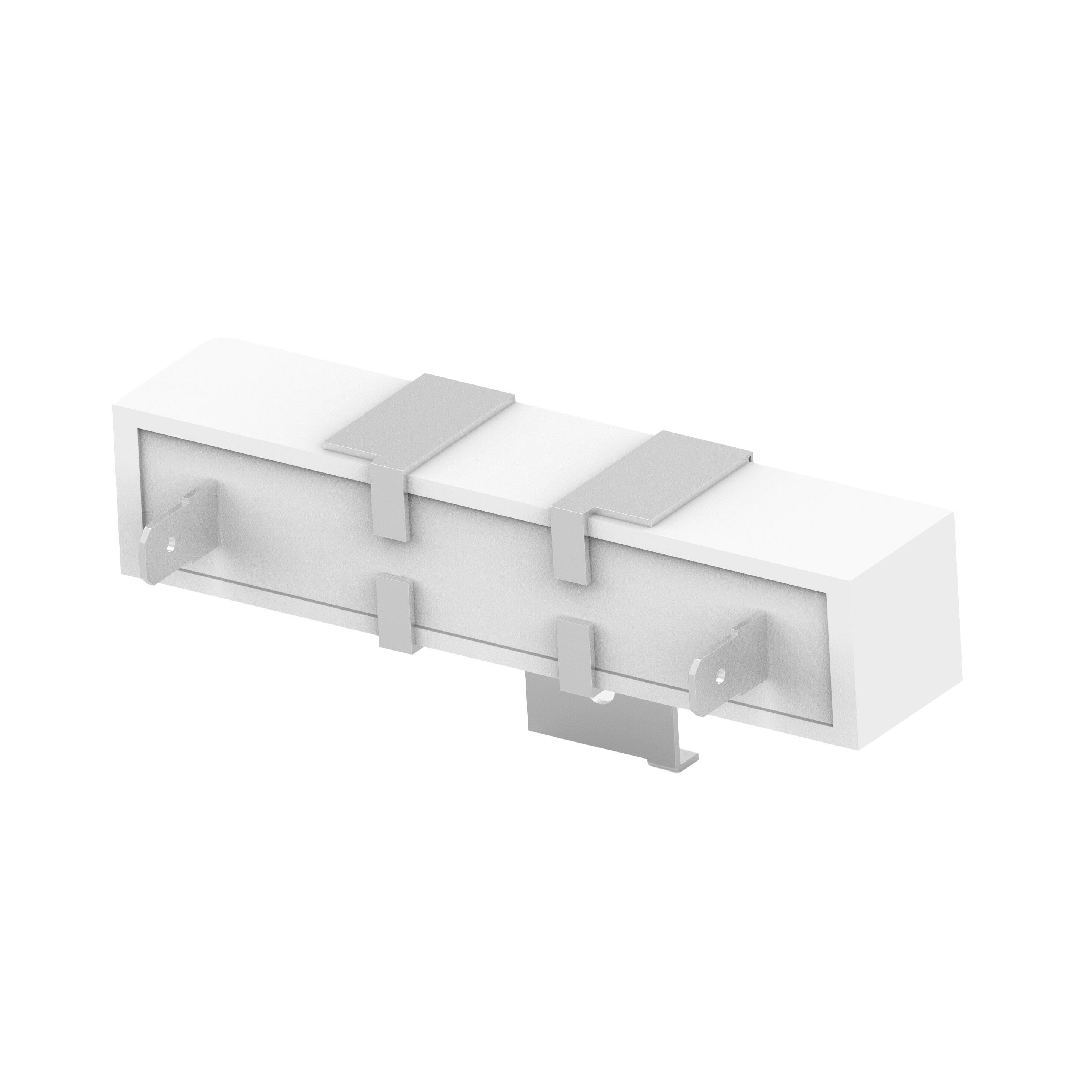











 PMDM
PMDM
 YAGEO
YAGEO
 EMIT
EMIT